The Worldwide Organic Cotton Production Industry: History, Trends, Opportunities and Challenges
2023/6/8
The Worldwide Organic Cotton Production Industry: History, Trends, Opportunities and Challenges
Organic cotton is a type of cotton that is grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, genetically modified seeds, or other chemicals. It is certified by independent organizations that verify that the farmers follow certain standards and practices that protect the environment, the workers, and the consumers. Although organic cotton represents only 1-2% of global cotton production, it is growing in demand and popularity among consumers who are looking for more sustainable and ethical products.
In this article, we will explore the worldwide organic cotton production industry, its main producing countries, trends, success stories, and any other important information that apparel brands/manufacturers/designers should know. We will also provide some sources of data and statistics that can help you understand the market better and make informed decisions.
The Evolution of Organic Cotton Production
Organic cotton production has a long history that dates back centuries. However, it wasn't until the 20th century that organic cotton production began to gain momentum as a sustainable alternative to conventional cotton farming. From its ancient origins to its modern-day success, organic cotton production has come a long way.
Early Origins
The history of organic cotton production can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Incas and the Egyptians, who cultivated cotton without the use of synthetic fertilizers or pesticides. However, it wasn't until the 1900s that the idea of organic farming began to take shape.
The Beginning of Organic Farming
In the 1920s, an English agriculturalist named Sir Albert Howard pioneered the idea of organic farming as a holistic system that worked with nature rather than against it. Howard's approach emphasized the use of composting, crop rotation, and natural pest control methods, and it laid the foundation for modern organic farming practices.
The Development of Organic Cotton Production
In the 1980s, concerns about the environmental and health impacts of conventional cotton farming led to the emergence of organic cotton production as a viable alternative. Early pioneers in the organic cotton industry included Sally Fox, who began growing organic cotton in California in the 1980s, and the Texas Organic Cotton Marketing Cooperative, which was founded in 1993.
Key Milestones
The establishment of standards and certification systems for organic cotton, such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS), which was launched in 2006 and covers the entire supply chain from farm to final product.
The creation of networks and platforms for collaboration and advocacy among organic cotton stakeholders, such as the Organic Cotton Accelerator (OCA), which was founded in 2014 and aims to improve the sustainability and profitability of organic cotton farming.
The Rise of Certification
As organic cotton production grew in popularity, the need for certification standards became increasingly important. In 1991, the International Federation of Organic Agriculture Movements (IFOAM) established the first set of international organic standards. Today, several certification organizations, such as the Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) and the Organic Content Standard (OCS), provide certification for organic cotton production.
The evolution of organic cotton production is a story of human ingenuity, innovation, and perseverance. From its ancient origins to its modern-day success, organic cotton has come a long way. However, there is still much work to be done to ensure that organic cotton production continues to thrive and that it remains a sustainable alternative to conventional cotton farming.
Main Producing Countries
According to the Textile Exchange Organic Cotton Market Report 2022, the largest producers of organic cotton by volume in 2020/21 are India (38%), Turkey (24%), China (10%), and Kyrgyzstan (9%). These four countries account for more than 80% of the global organic cotton production volume. Other significant producers include Tanzania - 6%, Kazakhstan - 4%, Tajikistan - 4%, United States - 2%.
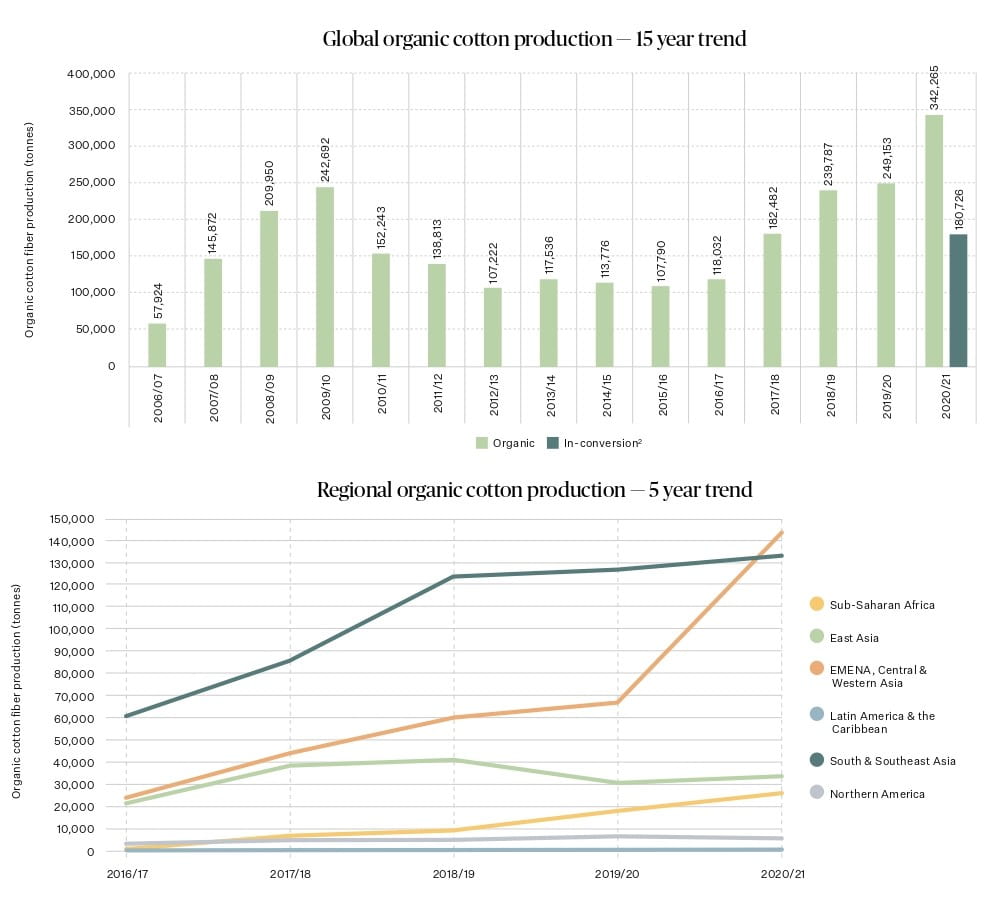
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P19
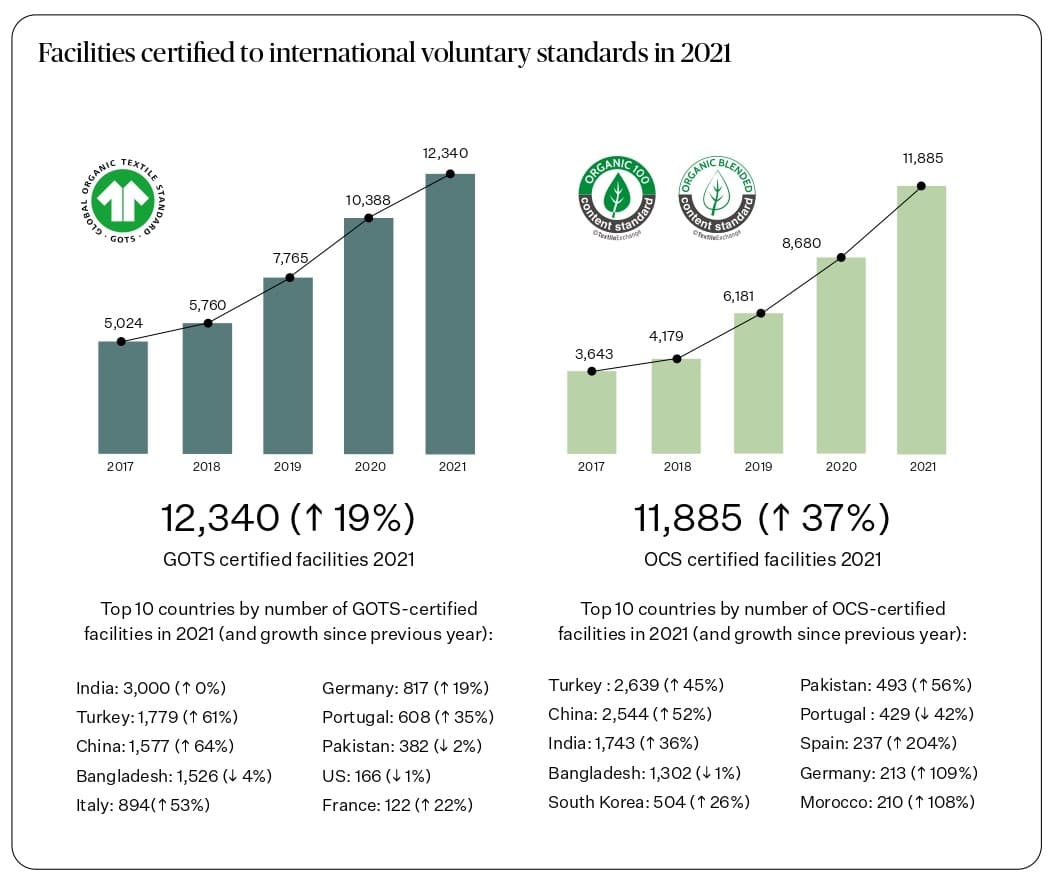
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P11
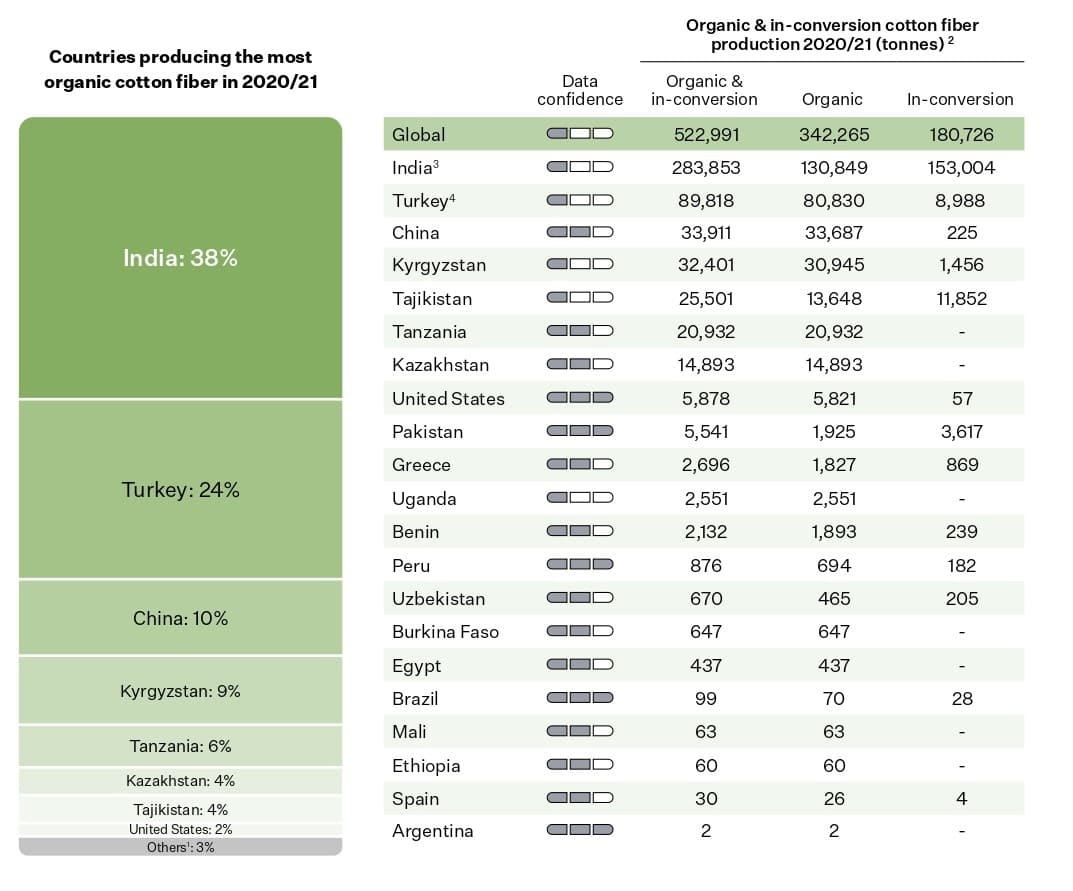
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P18
India is the world leader in organic cotton production, with more than 600,000 farmers involved in the sector. India has a long history and tradition of organic farming, as well as a strong domestic market for organic products. India also exports organic cotton to many countries, especially in Europe and North America.
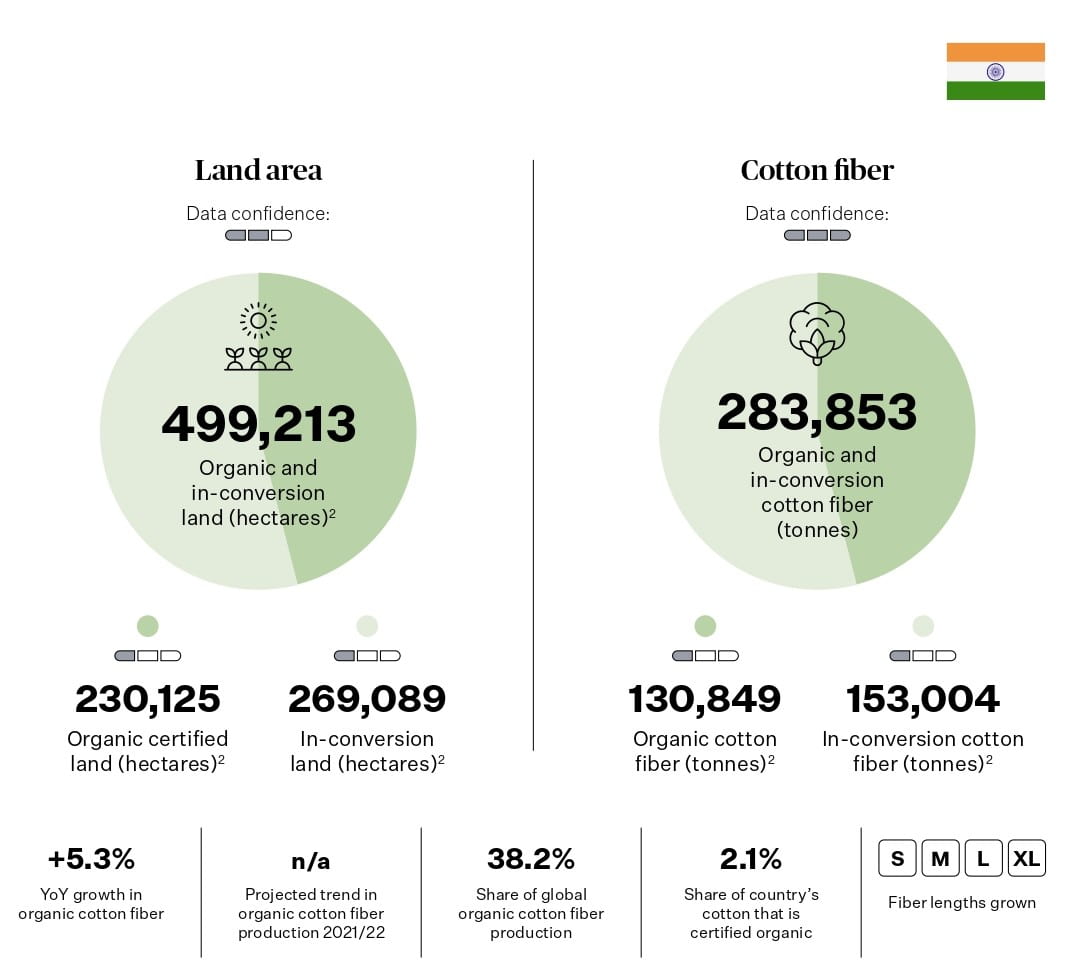
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P51
Turkey is the second largest producer of organic cotton, and also a major textile hub in Europe and Asia. Turkey has a well-developed organic cotton supply chain, with many certified mills, factories, and brands. Turkey also has a strong domestic market for organic products, as well as a strategic location for exporting to neighboring countries.
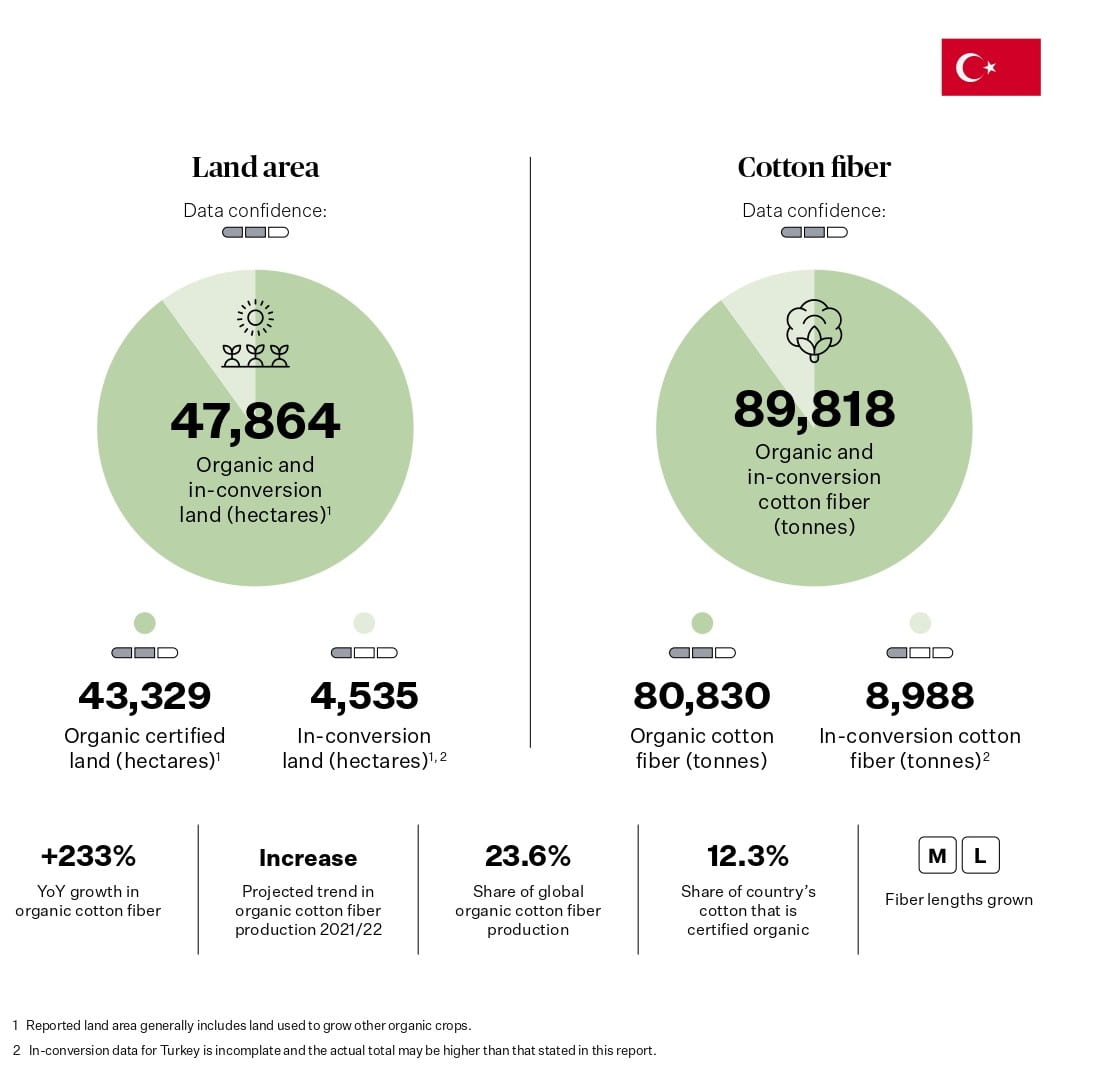
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P47
China is the third largest producer of organic cotton, and also the largest consumer of conventional cotton. China has been investing in organic cotton as a way to reduce its environmental impact and meet the growing demand from domestic and international customers. China has a diverse range of organic cotton products, from raw fiber to finished garments.

Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P38
Kyrgyzstan is the fourth largest producer of organic cotton, and one of the few countries in the world where all cotton production is organic. Kyrgyzstan has a unique system of community-based organic certification, which empowers smallholder farmers and ensures traceability and transparency. Kyrgyzstan also benefits from preferential trade agreements with the European Union and other markets.
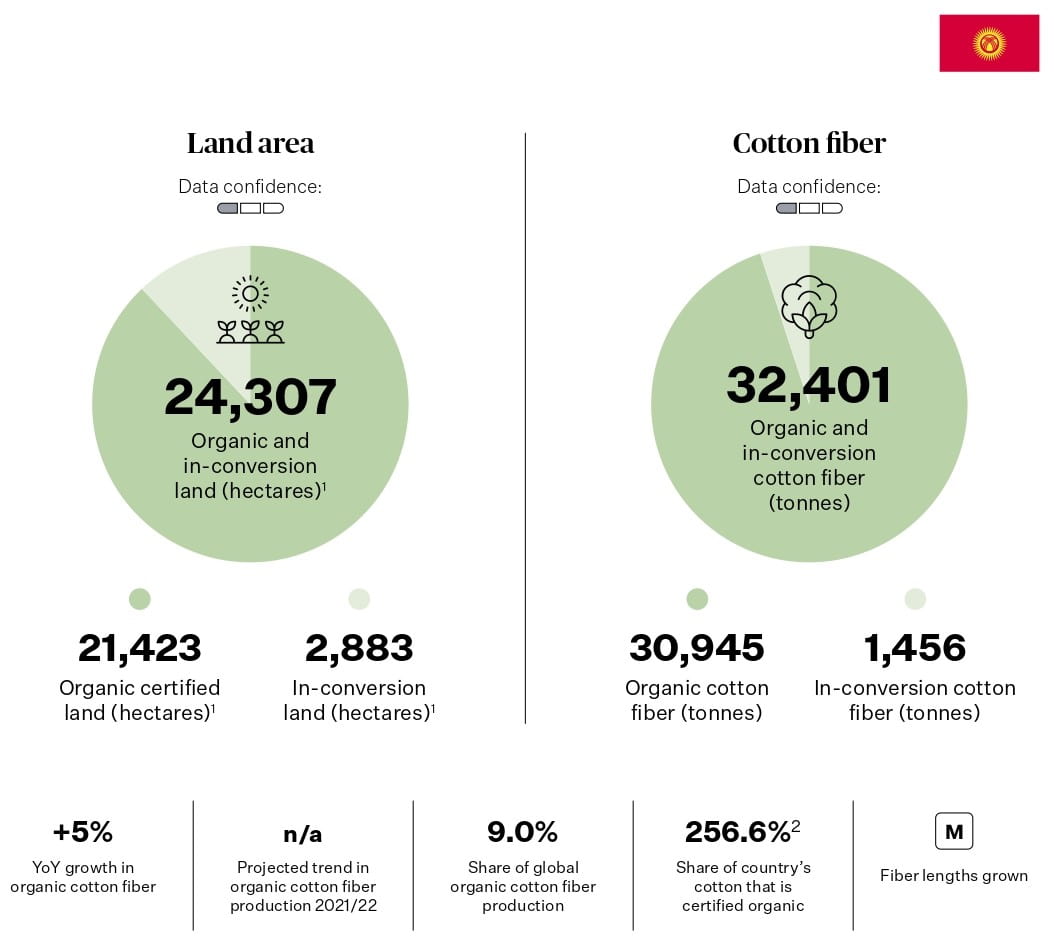
Source: Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. P44
The worldwide organic cotton production industry is driven by several trends that reflect the changing consumer preferences and expectations, as well as the challenges and opportunities faced by the farmers and businesses involved in the sector.
Trends and Opportunities

Growing Demand for Organic Cotton
The increasing demand for organic cotton products is driven by the growing awareness of consumers about the environmental and social benefits of organic cotton, and by the commitment of more brands to source organic cotton for their collections. With the increasing focus of consumers on traceability and transparency in the supply chain, many companies are implementing systems to track their cotton from farm to finished product and provide this information to consumers.
Achieving supply chain transparency is critical for the organic cotton industry, providing benefits for both producers and consumers. Producers can identify inefficiencies and reduce waste, leading to cost savings and increased productivity, while consumers can make informed purchasing decisions that build trust and increase brand loyalty.
However, the organic cotton industry faces challenges related to the complexity of supply chains, lack of standardization and regulation, and cost of implementing traceability systems. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration and commitment from all stakeholders. One solution for achieving greater traceability is through the use of blockchain technology, which can create an unalterable record of where the cotton was grown, how it was transported and processed, and where it ended up, thus building consumer trust and confidence in organic cotton products.
For instance, Walmart partnered with IBM to develop a blockchain-based system for tracking food products from farm to store, which has helped to reduce the time it takes to trace the origin of contaminated food from days to seconds. Similarly, the luxury fashion brand Stella McCartney partnered with Google to track the environmental impact of cotton and viscose, two of the most commonly used fibers in clothing. Their goal was to create a tool that could quantify even the most obscure links in the fashion supply chain.
Diversification of Organic Cotton Products
Another trend in the organic cotton industry is organic cotton is not only used for clothing, but also for a wide range of products such as home textiles, personal care items, accessories, toys, and more. Here are a few examples:
1. Bedding and linens: Brands like Coyuchi and Boll & Branch offer organic cotton sheets, duvets, and other bedding options.
2. Personal care products: Companies like Dr. Bronner's and The Honest Company offer organic cotton swabs and wipes, while Natracare and Maxim produce organic cotton tampons and pads.
3. Baby products: Brands like Burt's Bees Baby and Hanna Andersson offer organic cotton clothing, blankets, and other baby accessories.
4. Home goods: Companies like West Elm and Pottery Barn offer organic cotton towels and other home textiles.
5. Accessories: Brands like Patagonia and Lululemon offer organic cotton hats, scarves, and other accessories.
6. Toys: Companies like Under the Nile and Green Toys offer organic cotton stuffed animals and other toys.
The diversification of organic cotton products offers more opportunities for innovation and differentiation for manufacturers, apparel brands and designers who want to cater to different segments and niches of the market.
The Growing Trend of Regenerative Agriculture
In recent years, the movement towards regenerative agriculture practices in organic cotton farming has been growing in popularity. Regenerative agriculture is an approach that aims to enhance the health of soil, promote biodiversity, and increase ecological resilience. This method involves using techniques such as crop rotation, reduced tillage, and cover cropping, which can help sequester carbon in the soil. Carbon sequestration has been shown to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and studies have found that regenerative agriculture can have a greater impact on carbon sequestration than traditional organic farming practices. By adopting regenerative agriculture practices, farmers can contribute to mitigating the effects of climate change while promoting sustainable farming practices.
Several organic cotton farming communities around the world have embraced regenerative agriculture practices. Some of the techniques used by these communities include intercropping, agroforestry, and rotational grazing.
In India, the state of Maharashtra is one of the largest organic cotton farming communities, with more than 125,000 farmers. Other major organic cotton-producing states in India include Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan. In Turkey, the Aegean region is the largest organic cotton farming community, accounting for more than 70% of Turkey's organic cotton production.
These farming communities have made significant contributions to the growth and development of the organic cotton industry, providing high-quality organic cotton for a wide range of products.
The Role of Organic Cotton in Circular Textile Economy
Finally, there is a growing trend towards circularity in the textile industry. Circularity has become a buzzword in the textile industry, referring to the design of products and production systems that minimize waste and pollution while maximizing the reuse, recycling, and regeneration of materials. In fashion, circularity is a concept that can have a profound impact on reducing the industry's environmental footprint.
There are several methods to achieve circularity in the fashion industry, such as closed-loop production systems, product design for disassembly, and extended producer responsibility. These methods focus on reducing waste, increasing resource efficiency, and promoting sustainable economic growth. For example, closed-loop production systems aim to keep materials and products in use for as long as possible by recycling and reusing them, while product design for disassembly makes it easier to separate and recycle components at the end of their life.
Organic cotton can play a crucial role in the circular economy of the fashion industry. By growing cotton without synthetic inputs, organic cotton is a renewable resource that can be recycled, composted, or repurposed at the end of its life, contributing to a more sustainable and circular textile economy. Furthermore, small-scale farmers who grow organic cotton can benefit from fair trade practices, which ensure they receive a fair price for their products.
These practices can reduce waste, increase resource efficiency, and promote sustainable economic growth, benefiting both producers and consumers. By incorporating organic cotton into circular production and design systems, the industry can work towards a more sustainable and responsible future.
(Regarding more information on Circular Textiles & Circular Economy, you can read our article Fast Fashion VS Circular Textile).
Challenges Facing the Organic Cotton Production Industry
While the organic cotton production industry presents several opportunities for stakeholders, it also faces numerous challenges. Here are some of the challenges facing the industry:

High Production Costs
Organic cotton production is a labor-intensive process, which makes it more expensive than conventional cotton production. The cost of organic farming practices such as crop rotation, composting, and natural pest control, among others, can be quite high. This means that organic cotton farmers may not always be able to compete effectively with conventional cotton farmers in terms of pricing.
Lower Yields
Organic cotton production typically yields lower than conventional cotton production due to the absence of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This can affect the profitability of organic cotton farming and hinder its adoption by farmers.
Lack of Supply Chain Transparency
Verifying the authenticity of organic cotton products can be challenging due to the lack of transparency in the supply chain. It can be difficult to trace the origin of cotton from farm to finished product, which makes it harder for consumers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Limited Supply Chain Infrastructure
Organic cotton requires special handling and processing, which means that supply chain infrastructure must be in place to accommodate it. However, in many parts of the world, there is limited infrastructure to support organic cotton production, which makes it difficult for farmers to access markets for their products.
Limited Availability and Demand
Based on the findings of Textile Exchange's 2021 Organic Cotton Market Report, organic cotton production only accounted for approximately 1.4% of the total cotton production worldwide in the 2020/21 harvest season. Despite the growing demand for sustainable cotton, organic cotton still represents a small portion of the global cotton market due to the dominance of conventional cotton. This limited production of organic cotton can hinder its availability in the market, making it more challenging for brands and consumers to access sustainable cotton alternatives.
Consumer Education
Organic cotton is still a relatively new concept for many consumers. This means that there is a need for education to help consumers understand the benefits of organic cotton and why it is worth paying more for. Consumer education can be a costly and time-consuming process, which can be a challenge for the industry.
Competition from Synthetic Fibers
Synthetic fibers such as polyester and nylon are cheaper to produce than organic cotton. As a result, they are often used as alternatives to cotton in many textile applications. This means that the organic cotton industry must compete with synthetic fibers for market share, which can be challenging given the price differential.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to organic cotton production. Extreme weather events such as droughts and floods can cause significant damage to crops, which can result in reduced yields and quality. Climate change can also lead to changes in pest and disease patterns, which can make it more difficult for organic cotton farmers to control pests and diseases.
To achieve a sustainable and prosperous organic cotton production industry, all stakeholders must collaborate to address the challenges the industry faces. Investing in research and development to improve organic farming practices can lead to higher yields and lower production costs. Improving supply chain transparency and traceability can also build trust between stakeholders and increase consumer confidence in organic cotton products. Innovative solutions may involve creating new supply chain infrastructure and educating consumers about the benefits of organic cotton.
By working together, the organic cotton production industry has the potential to drive sustainable economic growth, promote social and environmental responsibility, and contribute to a more sustainable future for all.
In conclusion, the organic cotton production industry is a growing sector that presents both opportunities and challenges. Despite the challenges of higher costs and lower yields, organic cotton is becoming increasingly popular among consumers who value sustainability and social responsibility. By adopting innovative production methods, improving supply chain transparency, and promoting circularity, the industry can continue to grow and contribute to a more sustainable and equitable future.
Innovations in Organic Cotton Farming
To overcome these challenges and enhance sustainability and competitiveness, farmers and researchers are developing and adopting various innovations in technology and techniques.
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is one of the innovations being used in organic cotton farming. This technology involves using sensors, drones, satellites, and artificial intelligence to monitor and optimize crop growth, soil health, water use, pest management, and harvest timing. By using precision agriculture, organic cotton farmers can reduce their inputs, increase their yields, and enhance their environmental performance.
Biotechnology
Another innovation in organic cotton farming is biotechnology. This technique involves using genetic engineering or gene editing to create new varieties of organic cotton that are more resistant to pests, diseases, droughts, or salinity. Biotechnology can also help organic cotton farmers improve their fiber quality, color, and durability.
Agroecology
Agroecology is a farming technique that involves applying ecological principles and practices to design and manage organic cotton farming systems that are more diverse, resilient, and productive. By applying agroecology, organic cotton farmers can enhance their soil fertility, biodiversity, pest control, and climate adaptation. For example, intercropping involves planting different crops in the same field, which can improve soil health, reduce the risk of pest infestations, and increase yields.
Cover Cropping
Cover cropping is another technique gaining popularity in organic cotton farming. This technique involves planting a non-cash crop such as clover or rye between cotton growing seasons to improve soil health and prevent erosion. Cover crops can also help reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and herbicides, further improving the sustainability of organic cotton farming.
Innovations in organic cotton farming have the potential to enhance sustainability and competitiveness in the industry. By adopting these technologies and techniques, organic cotton farmers can improve their yields, reduce their costs, and contribute to a more sustainable future. As consumers continue to demand environmentally friendly products, the organic cotton industry will continue to grow, and these innovations will play a crucial role in its success.
Partner with Fanterco for Sustainable Fashion: Your Trusted Supplier of Organic Cotton
Fanterco is a Taiwan textile manufacturing solution provider of organic cotton committed to supporting the organic cotton industry and promoting sustainable fashion practices. We offer a wide range of high-quality products to meet the diverse needs of fashion brands and designers. Our focus on transparency and traceability ensures that our customers have access to accurate information about the origin and production of our organic cotton.
By partnering with us, you can elevate your fashion line with our eco-friendly and socially responsible materials. If you are looking to incorporate organic cotton into your fashion line, look no further than Fanterco. Contact us today to learn more about our products and how we can help you achieve your sustainability goals. We are always ready to collaborate and support your sustainable fashion practices.
Sources:
1. Textile Exchange. (2022). Organic Cotton Market Report 2021. https://textileexchange.org/app/uploads/2022/10/Textile-Exchange_OCMR_2022.pdf
2. Cotton Made in Africa. (CmiA.). Organic Cotton. https://cottonmadeinafrica.org/wp-content/uploads/Evaluation-of-CmiAs-WASH-projects-in-Cote-dIvoire-French-English.pdf
3. H&M. (2021). Sustainable Materials. https://hmgroup.com/sustainability/planet/sustainable-materials/organic-cotton.html
4. Levi Strauss & Co. (2021). Sustainable Cotton. https://www.levistrauss.com/sustainability/sourcing/sustainable-cotton/
5. Patagonia. (2021). Organic Cotton. https://www.patagonia.com/our-footprint/organic-cotton.html
6. Better Cotton Initiative Annual Report 2020. https://bettercotton.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/BCI_AnnualReport_2020_FINAL-WEB.pdf
7. Organic Cotton Accelerator Annual Report 2020. https://bettercotton.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/BCI-2020AnnualReport.pdf














